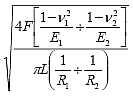Maximum Constant Pressure and Shear Stress Calculations. Line Contact |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Parameter |
Symbol |
Equation |
||||||||||||||||||
Contact half-width |
b |
|
||||||||||||||||||
Maximum Hertzian Contact Pressure |
Pmax |
Pmax = 2 * F ∕ π.l.b |
||||||||||||||||||
Maximum Contact Shear Stress |
Ʈmax |
Ʈmax = 0.3 * Pmax |
||||||||||||||||||
The Maximum Contact Shear Stress,Ʈmax, is at a depth below the Cam and Roller Surfaces at about Z = 0.786×b. You should make sure that the of case hardness depth is a minimum of 1.41×b, even better to make sure it is 2×b Typical Stress against Depth from Contact Surface |
||||||||||||||||||||
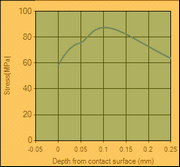 Stress vs Depth |
||||||||||||||||||||
Notes Modulus of elasticity (Young’s modulus): The rate-of-change of unit tensile or compressive stress with respect to unit tensile or compressive strain for the condition of uni-axial stress within the proportional limit. Typical values: Aluminum: 69 GPa ; Steel: 200GPa. Poisson’s ratio: The ratio of lateral unit strain to longitudinal unit strain under the condition of uniform and uni-axial longitudinal stress within the proportional limit. Typical values: 0.3. Proportional Limit: The largest value of stress up to which a linear relation still exist between stress and strain (Hooke’s Law). Cylindrical contact: The contact of two Cylinders parts where contact point turns to a rectangular area equal to a width 2b. Shear stress: A form of a stress acts parallel to the surface (cross section) which has a cutting nature. Stress: Average force per unit area which results strain of material. |
||||||||||||||||||||