EXAMPLE: Output Transmission Rigidity
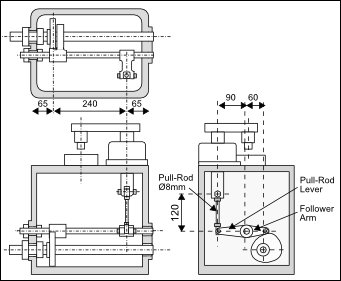 Design Arrangement of an Output-Transmission - from the cam-follower to the payload. |
A cam-driven mechanism is operated by a lever and pull-rod transmission with a stroke-increasing ratio of 1.5 : 1 , as shown in the image. A 60mm long follower arm is keyed to one end of a 20mm diameter steel pivot shaft on the other end of which is keyed a 90mm long pull-rod lever. That lever pulls a payload by means of an Φ8mm x 120mm long steel pull-rod. Find the overall transmission rigidity from the cam to the payload, assuming that the follower arm and pull-rod lever are stiff enough to be ignored in the calculation. |
||||||||
Working back from the payload to the cam: 1: Pull-Rod
This acts at the end of a 90mm long lever. Thus, the torsional rigidity referred to the pivot shaft (Equation 5 ())
2: Pivot shaft bending at pull-rod position Equation 8: Stiffness of Shaft Supported between two bearings. From Equation 8
Equation 5: Stiffness referred to the pivot shaft is:
3: Pivot Shaft Torsion Equation 1: The length of the shaft in torsion is 240mm. From Equation 1
4: Pivot Shaft Bending at Follower Position The shaft is symmetrical along its length and its stiffness in bending, S , at this position is the same as at the pull-rod position. The rigidity referred to the pivot shaft is therefore:
Overall Rigidity The overall torsional rigidity of the cam output transmission at the follower arm pivot pivot is:
This could be expressed as a linear stiffness at the follower roller by transposing Equation 5:
It is clear from the above figures that torsion of the pivot shaft is by far the most elastic element, showing that the transmission rigidity can be considerably improved, if necessary, by increasing the shaft diameter. Because shaft rigidity and stiffness are proportional to the fourth power of diameter, an increase from 20mm to 24mm would approximately double the overall rigidity. |
|||||||||