IMPORTANT : Before you analyze Contact-Force and Contact-Stress... ... reconfigure the model so that the Power flows from a drive-motor to the payload. |
Payload Signatures
Payload is the superposition (addition) of the different types of force that act between the Cam-Profile and Follower-Profile.
Payload Signature is the payload plotted over one machine cycle or cam rotation.
The Payload Signature is a function of machine-angle and of machine-speed.
Payload Types
|
Payload Type |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Constant Load |
Gravity, Friction*, Spring Pre-load. |
|
Load Proportional to Follower Displacement |
Spring Force |
|
Load Proportional to Follower Velocity. |
Viscosity, Air-Cylinder |
|
Load Proportional to Follower Acceleration |
Inertia Forces
|
|
Load as a 'Special Function' |
'Power' stroke of an Engine |
* Friction-force is a function of the contact force, and, thus, it is not necessarily a constant value. Friction-forces are actually very difficult to calculate correctly. Thus, it is modeled as a Constant-Force opposite to the direction of motion. |
||
Importance of Machine Speed
In the case of the example below, the payload is a superposition of three load types:
•Constant Force (Green), for example a Gravity, Air-Cylinder Spring-Pre-load
•Displacement Force (Blue), for example a Spring Force
•Acceleration Force (Magenta), for example an Inertia Force
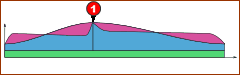 Cam forces at 'Low Speed'. |
When we plot the force over one machine cycle, but at two different machine speeds: Low-Speed: •The maximum payload is at the maximum displacement of the spring and Follower •The acceleration force is low. High-Speed: •The maximum payload is at the large positive acceleration •The minimum payload is a force that is less than zero |
|---|---|
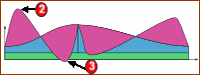 Cam forces at 'High Speed'. |