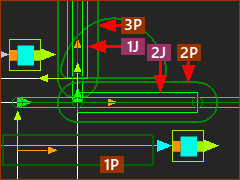
Piggyback Sliders
The Piggyback Slider configuration has two Sliders: •Slider(A) : moves along the X-axis* of the Mechanism-Plane •Slider(B) : moves relative to Slider(A), and parallel to the Y-axis of Slider(A) * The two Sliders do not need to be parallel to the X-axis or the Y-axis, or even perpendicular to each other. We use the X and Y-axis directions for convenience only. They can be, for example, in the Radial and Tangential directions of a circle. |
Mechanical Systems that have an XY Motion :
Piggyback Sliders E.g. Gantry Robot
The Piggyback Sliders are usually perpendicular (normal, 90º, orthogonal) to each other. •A servo-motor that drives an axis has a linear relationship with the motion of each of the Piggyback Sliders. •The servo-motor can drive different linear-technologies: Pulley & Belt, Ball-Screw & Nut, Rack & Pinion, Linear-Servomotor, ... . |
Piggyback Sliders and Dyads
The Piggyback Sliders are usually perpendicular (normal, 90º, orthogonal) to each other. •Connect a dyad from the machine-frame and each Piggyback-Slider. •Add a cam or servo-motor to drive a Part in each dyad •Inverse-kinematics calculates the motion of each follower or servo-motor from the motion designed for each Piggyback Sliders - See Step 11.2 |
Translating Beam (a Part that moves on the Mechanism-Plane but does not rotate)
The Piggyback Sliders are usually perpendicular (normal, 90º, orthogonal) to each other. •In this case, the Sliders are not used in the physical machine. They are used to design the XY motion only. •Design a mechanism with a translating-beam that is not physically connected to the machine-frame or the Piggyback Sliders. •Look at this video to see the design. |
Add Piggyback Sliders - Quick Instructions
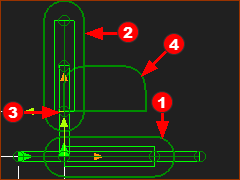 |
Quick Instructions:
|
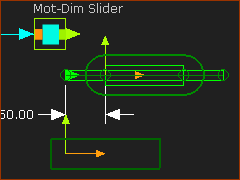
Add Piggyback Sliders - Detailed Instructions
 |
Add Slider-X
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
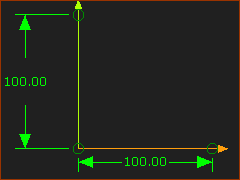 |
Edit Slider-X, Add a Vertical Line
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Add the Slider-Y
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Get Motions for the Sliders
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
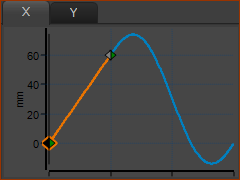 |
Run menu > Cycle (or ALT+C) Motion-X
Link Motion-X to a Motion FB to connect a wire to the Motion-Dimension FB to move Slider-X. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Motion-Y
Link Motion-Y to a different Motion FB and connect a wire to the Motion-Dimension FB to move Slider-Y. |
Degrees-of-Freedom of Piggyback Sliders
|
Degrees-of-Freedom and Mobility
|
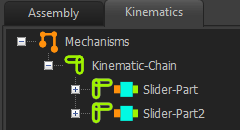
Kinematics Tree of Piggyback Sliders
|
Kinematics-Tree for Piggyback Sliders.
|
Machines that use Piggyback Sliders
X-Y Gantry Robot The movements of the Sliders plot the drawing. The slider positions are linearly related to the XY-Path. |