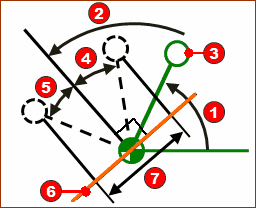
CV (Constant-Velocity) Inverse Crank
Motion-Description
Motion-Values
You CANNOT control the:
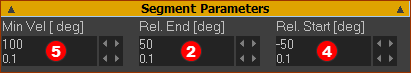
Segment Parameters
Segment-Range
|
||||||||
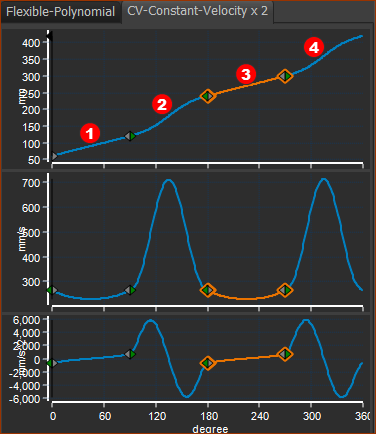 Example motion with 2 x CV Inverse-Crank motion-laws |
||||||||
EXAMPLE Two CV Inverse Crank segments in one Motion. Segment •X-axis : 0 to 90º Segment Parameters are: •Angle of Minimum Velocity = 90º •Relative Start Angle = –30º •Relative End = 30º With these Parameters: •X-axis = 0º ; Y–axis = 60º. •X-axis =90 ; Y–axis = 120º Segment •X-axis : 90 to 180º •Y-axis at Start P=120. V, A, J flow from the end of the Constant-Crank-Velocity Segment. •Y-axis at End 240º Segment •X-axis : 180 to 270º Segment Parameters are: •Angle of Minimum Velocity = 270º •Relative Start Angle = –30º •Relative End = 30º With these Parameters: •X-axis = 180º ; Y–axis = 240º •X-axis = 270 ; Y–axis = 300º Segment •X-axis : 90 to 180º •Y-axis P at Start = 300º. V, A, J flow from the end of the Constant-Crank-Velocity Segment. •Y=axis at End = 420º. |