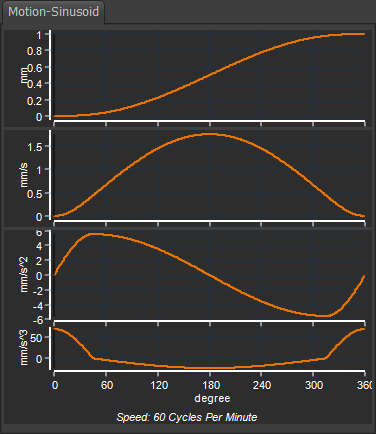
The Modified Sinusoid motion-law has relatively low peak velocity, and low jerk at crossover.
Dynamic Performance
The Modified Sine is a good general purpose motion-law particularly in applications where the period ratio is between 5 and 10, and if the input drive is flexible or it has backlash. It performs well with respect to residual vibration after the segment is complete.
Pressure Angle Considerations
It produces a relatively small pressure angle, and so it can give a smaller cam for a given lift and pre-prescribed maximum pressure angle than other motion-laws.
Drive Torques
The nominal drive torque characteristics and the actual torque values are low. The low peak values and the smooth variation of drive torque further emphasize the suitability of this motion-law where the input drive is flexible or has backlash.
|