Preparation for Kinetostatic Analysis and Dynamic Analysis
Before you can do a Kinetostatic (force) and/or the Dynamic analysis of a kinematic-chain, you need to enter these mass properties for each Part:
•Mass
•Mass Moment of Inertia about its center-of-mass (or enter its Radius of Gyration)
•Center of Mass relative to the CAD-Lines Coordinate System.
Use the CAD-Line dialog to enter the parameters. See CAD-Line dialog : Mass-Properties tab
We refer the Mass and the Mass Moment of Inertia of each Part to the Power Source of the degree-of-freedom whose dynamic response you want to analyze.
The Power Source must overcome different loading types, which we define with Torque Coefficients.
We calculate the Inertia Coefficients at each step in the machine-cycle.
The Inertia Coefficients are a function of the position, velocity, and acceleration of the kinematic-chain.
The Inertia Coefficients are usually not constant in the machine-cycle.
The Inertia Coefficients we calculate are:
•Gravity Coefficient: - inertia needed to overcome the Gravitational Torque
•Velocity Squared Coefficient - Inertia proportional to the square of the in Velocity
•Acceleration Inertia - the the inertia that must accelerate.
We plot the Inertia Coefficients for the complete machine-cycle, which we plot in the Inertia Coefficients tab
From the Inertia Coefficients we can also calculate the Torque required for each 'loading' type at each step in the machine-cycle. We plot the Torque for the complete machine cycle in the Torque Contributions tab.
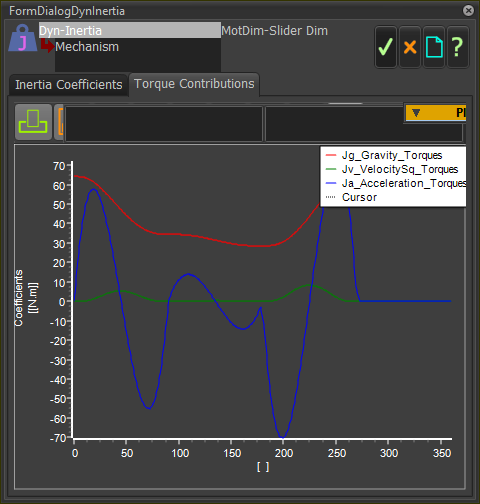
Torques required for each Inertia Coefficient.