Sine-Squared Cam-Law, Motion-Law
Motion Description
Motion-ValuesYou CAN control the:
You CANNOT control the:
Segment Parameters
Segment-Range
See also : See also : |
|||||||||
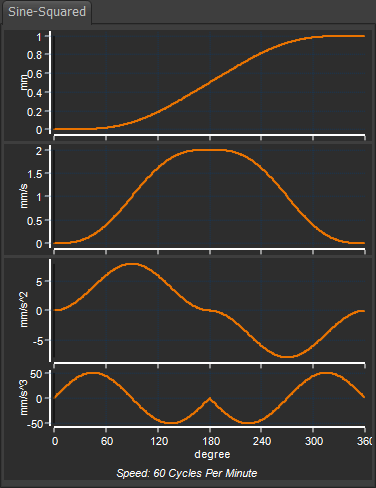 Sine-Squared Motion-Law / Cam-Law Motion-Law Coefficients
Application Notes
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Navigation: MotionDesigner Reference & User Interface > Motion Laws / Cam-Laws for Segments > Sine-Squared Motion-Law |
Motion Description
Motion-ValuesYou CAN control the:
You CANNOT control the:
Segment Parameters
Segment-Range
See also : See also : |
|||||||||
 Sine-Squared Motion-Law / Cam-Law Motion-Law Coefficients
Application Notes
|