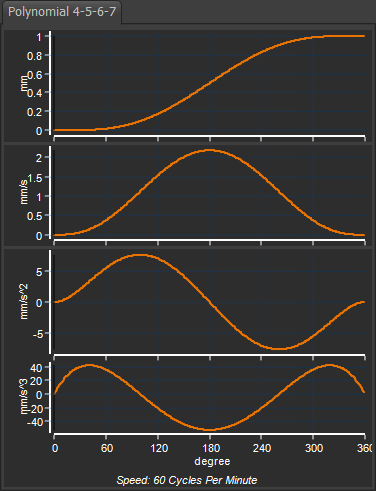
A Traditional Motion-Law. Its name is often reduced to Poly-4567.
A motion with continuous Velocity and Acceleration, from start to end. The Jerk is finite at its start and end. It has finite Jerk throughout.
It has a high maximum-velocity, high maximum-acceleration, high . Only the Modified-Trapezoidal (of those with finite Jerk) has a greater crossover jerk.
At its start and end, the Y-axis values do not change much with a significant X–axis change - e.g. 0.02% Y-axis with 5% X-axis change.
Therefore, a cam needs accurate machine if it is to reproduce this segment. A larger cam often helps, or an encoder with a high resolution.
If possible, increase the segment-width to reduce its maximum Velocity, Acceleration and Jerk values.
|