About the Kinematics-Tree
The Kinematics-Tree is the kinematic-structure of each kinematic-chain in the active Mechanism-Editor.
We compile the kinematic-chains from the kinematic-elements that are kinematically-defined.
Notes:
If you cannot see or explore the elements in the Kinematics-Tree, click Rebuild now. If you click to explore a kinematic-chain in the Kinematics-Tree: •the kinematic-chain expands to the show the kinematic-elements in the kinematic-chain, •the color of the kinematic elements in the kinematic-chain change to the “Selected Color” - see Application-Settings > Graphics > Display Color. To collapse the kinematic-chain again, you must click in the graphics-area in an empty space. •You can right-click on any kinematic-chain to Configure the Power Source |
Example
Note: If you cannot see “Mechanisms”, or explore the Kinematics-Tree, click Rebuild now. The structure of the Kinematics-Tree is: ► Mechanisms: ► Kinematic-Chains ► Kinematic Sub-assemblies ► Kinematic Elements ►Unsolved Mechs
The Mobility of these kinematic-chains is zero(0). They are kinematically-defined (solved). You can explore the kinematic-chains to find Kinematic Sub-Assemblies and kinematic elements (see below)
These kinematic-chains have a mobility that is greater than zero(0). The kinematic-chains are not kinematically-defined. |
|||
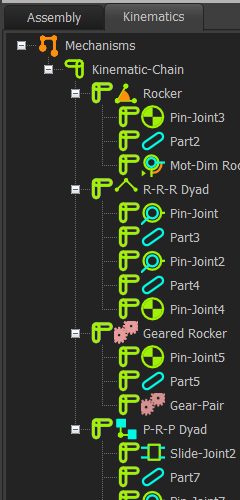 Example: Kinematics-Tree in Element-Explorer |
Kinematic-Sub-Assemblies (Solved Mechanisms ONLY): These are compiled as: a.Rockers b.Sliders 2.Dyads The type of Dyad is identified by its three joints, denoted with a letter: R = Revolute-Joint = Pin-Joint P = Prismatic-Joint = Slide-Joint S = Spherical-Joint = Ball-Joint a. R-R-R b. R-R-P c. R-P-R d. P-R-P e. R-P-P f. Ram-R g. Ram-P h. S-S-R i. S-S-P |
||