Flexible-Polynomial Cam-Law, Motion-Law
Motion Description
Motion-Values You CAN control the:
You CANNOT control the:
Segment Parameters
Segment-Range
VDI 2143 The German motion standard describes different motion-derivatives conditions (or transition) at the start and end of a segment. They summarize in a diagram, such as below, which is taken from a Siemens motion-control servo manual. Flexible Polynomial segments can satisfy all of the transition requirements, implied in the image below. 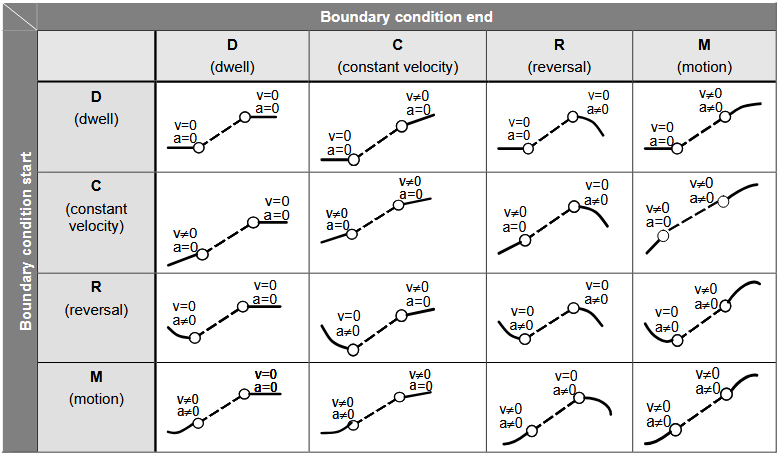 |
|||||
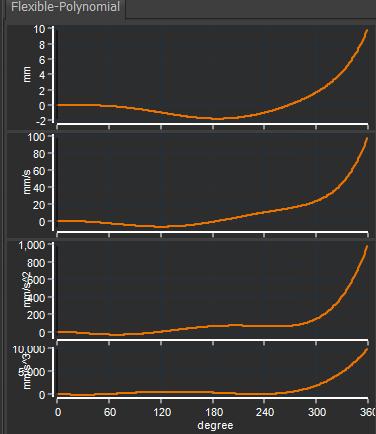 Flexible-Polynomial |